The xylem and phloem are conducting and supporting vascular tissues, and the vascular cambium is a lateral meristem that gives rise to the secondary vascular tissues, which constitute the secondary plant body. …a lateral meristem called the vascular cambium (Figure 8). The vascular cambium, which produces xylem and phloem cells, originates
The vascular cambium normally gives rise toPhellodermPeridermPrimary phloemSecondary xylem
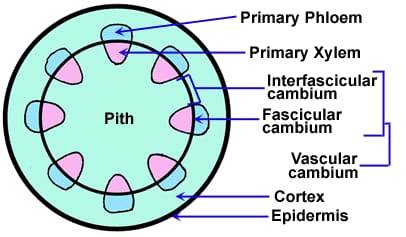
The activity of the vascular cambium gives rise to annual growth rings. During the spring growing season, cells of the secondary xylem have a large internal diameter and their primary cell walls are not extensively thickened. This is known as early wood, or spring wood. During the fall season, the secondary xylem develops thickened cell walls

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
a. It results from cell divisions in the vascular and cork cambia. b. It increases the length of the plant stem. c. It results from divisions in the apical meristem cells. d. It often produces phloem cells to the inside and xylem cells to the outside of the vascular cambium. Question 5a.

Source Image: britannica.com
Download Image
Vascular Cambium – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The cambium has been variously defined as follows: “The actively dividing layer of cells that lies between, and gives rise to, secondary xylem and phloem (vascular cambium)” (IAWA 1964); “A meristem with products of periclinal divisions commonly contributed in two directions and arranged in radial files.

Source Image: byjus.com
Download Image
The Vascular Cambium Gives Rise To _____.
The cambium has been variously defined as follows: “The actively dividing layer of cells that lies between, and gives rise to, secondary xylem and phloem (vascular cambium)” (IAWA 1964); “A meristem with products of periclinal divisions commonly contributed in two directions and arranged in radial files.
The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark .
Secondary Growth In Plants – Vascular Cambium And Cork Cambium
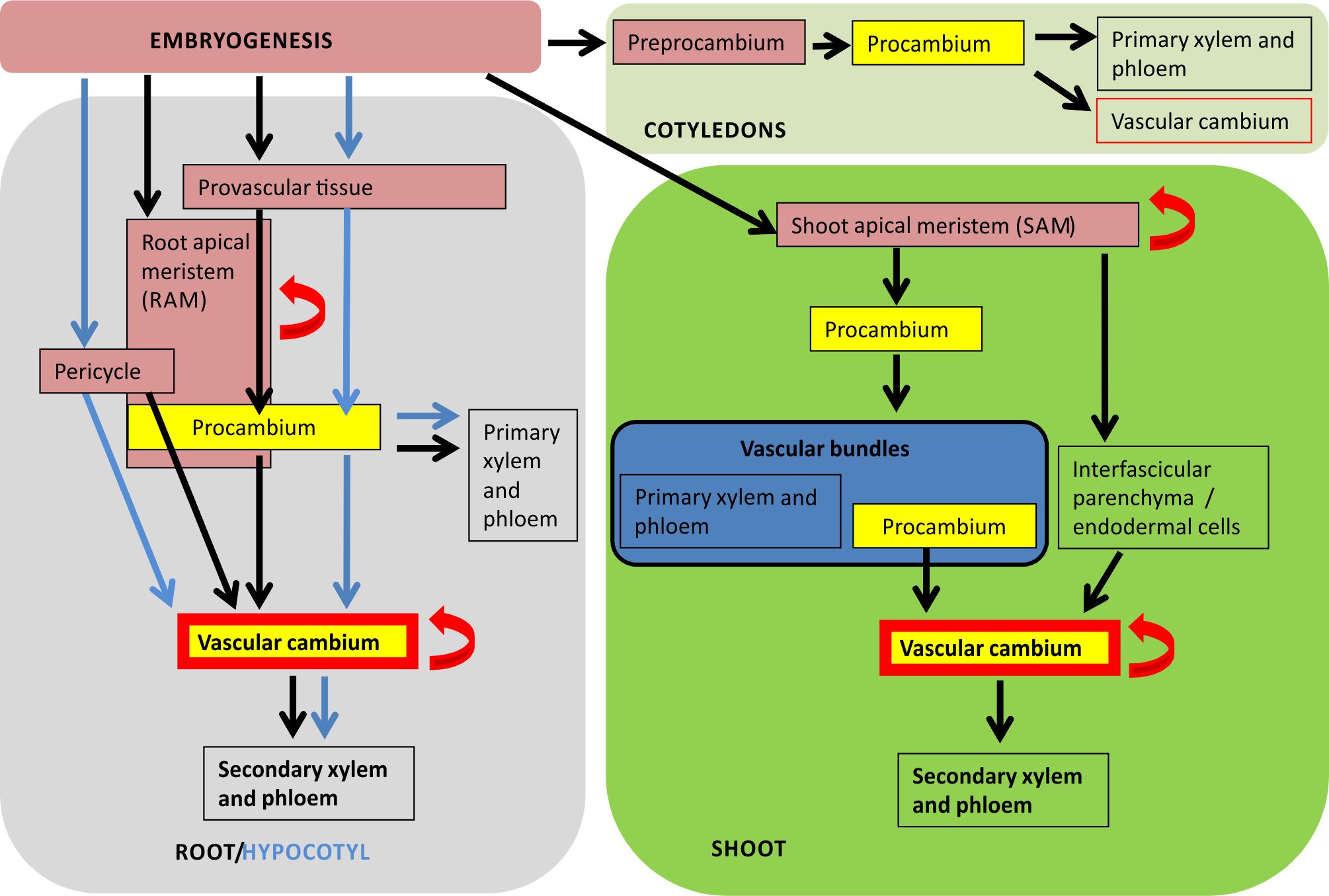
The vascular cambium is responsible for the lateral (secondary) growth of plants, a process which must be carefully regulated in order to ensure holistic development of the plant vasculature. Figure 1.
Secondary growth – Wikipedia
Source Image: en.wikipedia.org
Download Image
Cambium – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The vascular cambium is responsible for the lateral (secondary) growth of plants, a process which must be carefully regulated in order to ensure holistic development of the plant vasculature. Figure 1.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
The vascular cambium normally gives rise toPhellodermPeridermPrimary phloemSecondary xylem
The xylem and phloem are conducting and supporting vascular tissues, and the vascular cambium is a lateral meristem that gives rise to the secondary vascular tissues, which constitute the secondary plant body. …a lateral meristem called the vascular cambium (Figure 8). The vascular cambium, which produces xylem and phloem cells, originates

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Vascular Cambium – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
a. It results from cell divisions in the vascular and cork cambia. b. It increases the length of the plant stem. c. It results from divisions in the apical meristem cells. d. It often produces phloem cells to the inside and xylem cells to the outside of the vascular cambium. Question 5a.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Vascular Cambium Development
Solution Verified by Toppr Vascular cambium is a layer of meristematic tissue which is present between the primary xylem and primary phloem. It divides to form secondary xylem and phloem and helps in secondary growth and wood formation. So, the correct answer is option D. Was this answer helpful? 0 Similar Questions Q 1
Source Image: bioone.org
Download Image
MCQ ON SECONDARY GROWTH/VASCULAR CAMBIUM / SECONDARY GROWTH/ VASCULAR CAMBIUM class 11 for NEET – Biologysir
The cambium has been variously defined as follows: “The actively dividing layer of cells that lies between, and gives rise to, secondary xylem and phloem (vascular cambium)” (IAWA 1964); “A meristem with products of periclinal divisions commonly contributed in two directions and arranged in radial files.
Source Image: biologysir.com
Download Image
Plant tissues. Meristems. Vascular cambium. Atlas of plant and animal tissues.
The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain other vascular plants. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark .

Source Image: mmegias.webs.uvigo.es
Download Image
Cambium – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Plant tissues. Meristems. Vascular cambium. Atlas of plant and animal tissues.
The activity of the vascular cambium gives rise to annual growth rings. During the spring growing season, cells of the secondary xylem have a large internal diameter and their primary cell walls are not extensively thickened. This is known as early wood, or spring wood. During the fall season, the secondary xylem develops thickened cell walls
Vascular Cambium – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics MCQ ON SECONDARY GROWTH/VASCULAR CAMBIUM / SECONDARY GROWTH/ VASCULAR CAMBIUM class 11 for NEET – Biologysir
Solution Verified by Toppr Vascular cambium is a layer of meristematic tissue which is present between the primary xylem and primary phloem. It divides to form secondary xylem and phloem and helps in secondary growth and wood formation. So, the correct answer is option D. Was this answer helpful? 0 Similar Questions Q 1